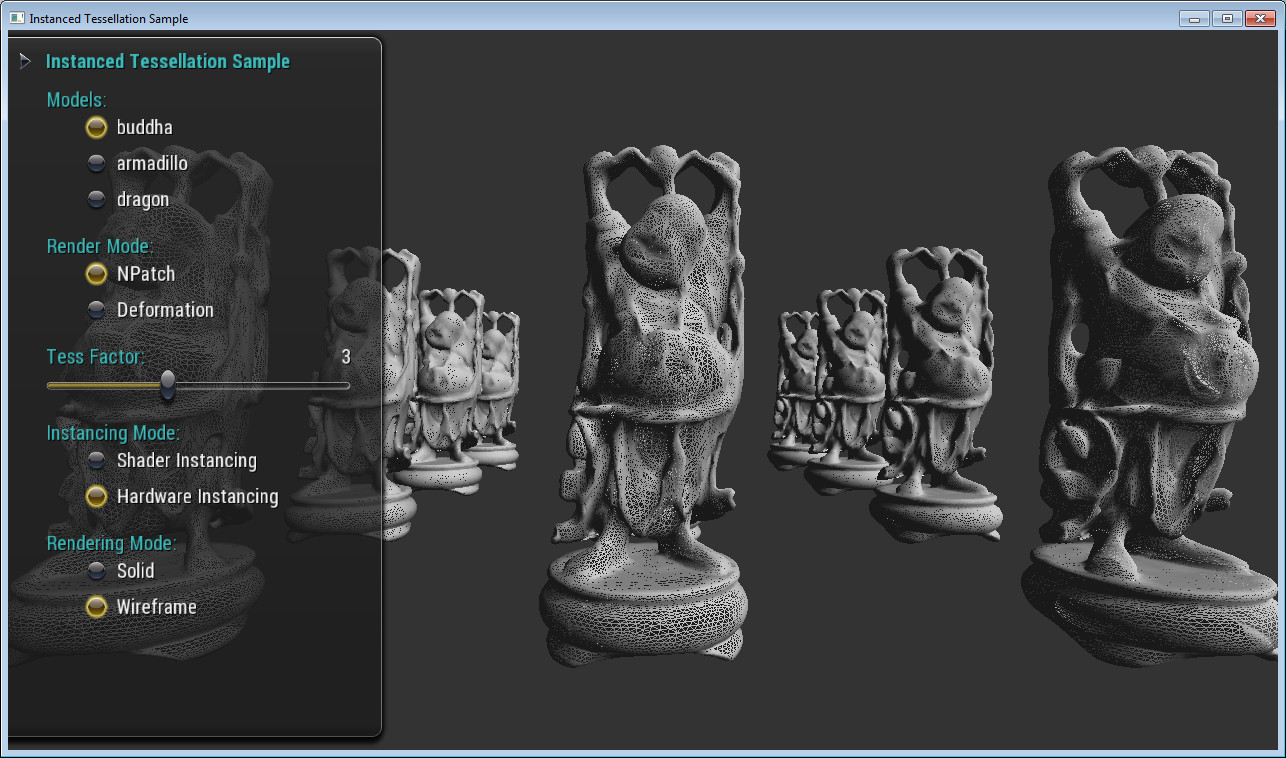
Instanced Tessellation Sample
Description
This sample demonstrates how instancing can be used to efficiently tessellate objects in real-time.
APIs Used
- glDrawElementsInstanced (or glDrawElementsInstancedARB, or glDrawElementsInstancedNV)
- glVertexAttribDivisor (or glVertexAttribDivisorARB, or glVertexAttribDivisorNV)
- GL_ARB_instanced_arrays [optional]
- GL_NV_draw_instanced [optional]
Shared User Interface
The Graphics samples all share a common app framework and certain user interface elements, centered around the "Tweakbar" panel on the left side of the screen which lets you interactively control certain variables in each sample.
To show and hide the Tweakbar, simply click or touch the triangular button positioned in the top-left of the view.
Technical Details
This sample demonstrates how instancing can be used to efficiently tessellate objects in real-time.
The basic idea behind instanced tessellation through instancing is this:
Create a vertex buffer object that contains a barycentric tessellation of a generic triangle.
Use instancing to draw an instance of this generic tessellation for every triangle of the object to be tessellated. For every instance the instance data will be the three 3D vertices and other vertex attributes of one of the current object-triangle be tessellated.
Inside a vertex program use the per instance data to evaluate whatever function using the additional per vertex barycentric coordinates.
Instancing Modes
There are two different modes of instancing demonstrated:
-
Software Instancing
One draw call is made for each triangle of the object. The per-instance data is passed as uniforms.
-
Hardware Instancing
One draw call is made to tessellate the whole object. Per-instance data comes in as vertex attributes using
glDrawElementsInstanced(),glEnableVertexAttribArray(),glVertexAttribPointer(), andglVertexAttribDivisor().
If the standard functions are not availableglVertexAttribDivisorARB/NVorglDrawElementsInstancedARB/NVare used.
Future Work
Two potential areas of future work/demonstration of this approach include:
- Dynamic tessellation based on size/LOD (for improved performance with small visuals, and improved quality with larger visuals, automatically)
- Use of displacement texture map for added details in the tessellated geometry.
See Also
- [Gruen05] Gruen H., 'Efficient Tessellation on the GPU through Instancing', In Journal Of Game Development Volume 1, Issue 3, Thomson Delmar Learning, December 2005.
- [Tatarinov08] Tatarinov, A., 'Instanced Tessellation in DirectX10'